
Stablecoins: The Anchors in the Storm of the Global Economic Crisis

The global economic landscape is undergoing a remarkable transformation as the winds of change sweep across borders and the concept of de-dollarization takes center stage. De-dollarization, a term that has gained significant traction in recent years, signifies a paradigm shift aimed at reducing the reliance on the U.S. dollar in international transactions. This phenomenon has captured the attention of economists, policymakers, and financial experts worldwide, heralding a potentially seismic shift in the global economic order.
A confluence of factors has fueled the momentum behind de-dollarization. Geopolitical tensions, trade wars, and the ascent of emerging economic powers have all played instrumental roles in reshaping the global economic climate. In the face of these multifaceted challenges, an intriguing alternative has emerged – stablecoins. These digital currencies, designed to maintain a stable value and minimize the volatility associated with traditional cryptocurrencies, have garnered considerable attention and are poised to disrupt the prevailing financial status quo.
This article aims to delve deep into the concept of stablecoins and elucidate their relevance in the context of de-dollarization. We will explore stablecoins comprehensively, and their potential implications for the global economic landscape. By shedding light on stablecoins and their intricate relationship with de-dollarization, this article aims to provide readers with a nuanced understanding of this fascinating development and its potential ramifications.
Historical Background: The Rise of Stablecoins
We can trace the rise of stablecoins as a significant player in digital currencies back to the early years of cryptocurrency development. While the concept of stable value digital currencies has existed for decades, the advent of Bitcoin in 2009 sparked a revolution in the financial world and laid the foundation for stablecoins to emerge.
In the early days of cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin gained attention for its decentralized nature and potential as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. However, its extreme price volatility hindered its practical use as a medium of exchange and store of value. Bitcoin's value fluctuated wildly, often experiencing significant price swings within short periods.
Recognizing this volatility as a significant barrier to mainstream adoption, developers, and innovators in cryptocurrency began to explore ways to create digital assets that maintained a stable value. Their goal was to bridge the gap between the advantages of cryptocurrencies, such as efficiency and borderless transactions, with the stability of traditional fiat currencies.
The first stablecoin, Tether (USDT), was introduced in 2014 to address this issue. Tether value was pegged to the U.S. dollar on a 1:1 ratio, providing stability and liquidity for cryptocurrency traders. Despite its controversies and regulatory scrutiny in subsequent years, Tether laid the groundwork for stablecoins and demonstrated the demand for digital assets with stable values.
As the cryptocurrency market matured, stablecoins gained traction, leading to the development of alternative types of stablecoins beyond fiat-collateralized ones. One notable development was the introduction of commodity-backed stablecoins. These stablecoins were designed to be backed by tangible assets like gold or oil, providing stability through the inherent value and strength of the underlying commodities.
Another type of stablecoin that emerged was algorithmic stablecoins. These stablecoins utilized complex algorithms and smart contracts to maintain their value stability. By automatically adjusting the supply and demand dynamics, algorithmic stablecoins aimed to achieve stability without needing direct collateralization.
The popularity and adoption of stablecoins expanded significantly in 2019, especially during periods of market volatility. Stablecoins offered a refuge for traders and investors seeking to preserve the value of their assets during market downturns. Their stability and liquidity made them an attractive alternative to holding traditional fiat currencies in uncertain economic conditions.
The concept of stablecoins gained further momentum with the rapid development of blockchain technology and the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi). Stablecoins became an integral part of the DeFi ecosystem, providing a stable and reliable medium of exchange, collateral, and liquidity in decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading platforms.
Today, stablecoins continue to evolve and diversify, with many projects and protocols entering the market. Governments and central banks have also started exploring the potential of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) as a form of stablecoin, aiming to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology while maintaining control over monetary policy.
The historical background of the rise of stablecoins showcases the ongoing quest for stability in digital currencies. From the early days of Bitcoin to the present era of DeFi and CBDCs, stablecoins have emerged as a promising solution to address the volatility inherent in cryptocurrencies. With each passing year, their relevance and importance in reshaping the global financial landscape continue to grow, making stablecoins a fascinating phenomenon to observe and explore.
Image credit: Markethive.com
The Great Currency Shift
De-dollarization, a trend gaining momentum in various parts of the world, is driven by geopolitical tensions, trade wars, and the rise of new economic powers. Countries like China, Russia, and Iran have been actively reducing their dependence on the U.S. dollar in international transactions, and this trend is expected to continue in the coming years. It will potentially have an impact on the stability of stablecoin.
The implications of de-dollarization for stablecoins and the broader crypto market appear chaotic at first glance. As the use of the U.S. dollar declines, demand for stablecoins pegged to the U.S. dollar, such as Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), may decrease. This shift in demand could create opportunities for alternative stablecoins pegged to other major currencies like the euro, yen, and yuan.
According to Bloomberg, the Chinese yuan surpassed the U.S. dollar as China's most popular cross-border currency, rising to a high of 48% of transactions from a low of almost 0% in 2010. This is an illustration of the de-dollarization process in operation.
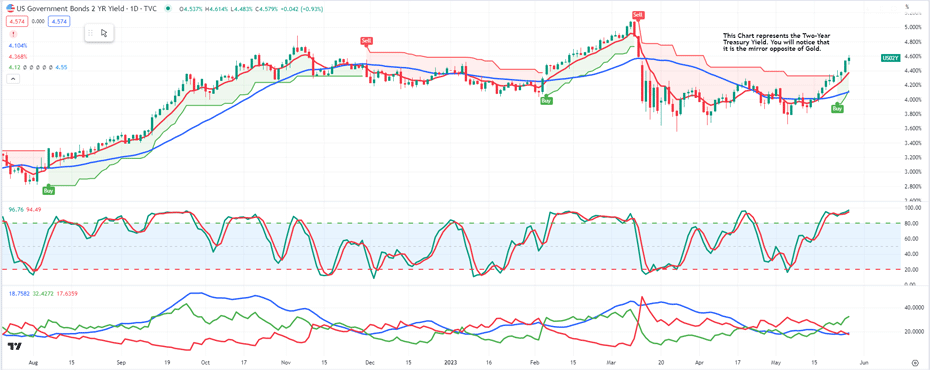
If the U.S. dollar loses its dominance as the global reserve currency, stablecoins pegged to the dollar would also lose their value and stability. To address this issue, there is a need for new stablecoin legislation to bolster the U.S. dollar. The Circle founder has suggested that Congress pass new stablecoin legislation to strengthen the greenback and prevent de-dollarisation's adverse effects on stablecoins. However, some experts argue that weaponizing the dollar will destroy its reserve currency status, leading to a further rise in de-dollarization
.png)
Image credit: Markethive.com
The Future of Stablecoins
Stablecoins can revolutionize how we conduct financial transactions, particularly in the context of de-dollarization. They can provide a secure and stable means of conducting cross-border transactions, investments, and hedging against currency fluctuations. However, governments must address several regulatory challenges and opportunities to ensure widespread adoption.
The future of U.S. pegged stablecoin will depend on several factors, including the continued dominance of the U.S. dollar in the global economy, the development of stablecoin regulations, and the ability of stablecoin to adapt to changing market conditions.
According to CoinMarketCap, every stablecoin with a market cap exceeding $1 billion is pegged to the U.S. dollar, which suggests that stablecoin's success is closely tied to the strength of the U.S. dollar. However, as de-dollarization continues to gain momentum, stablecoin may need to explore alternative pegs to maintain its stability and relevance in the market.
Stablecoins can be created in a variety of methods, but the ones that are currently in use are exogenous (backed by assets from outside the stablecoin's ecosystem) and fully/over-collateralized. Moving away from U.S. pegged stablecoins may likely not result in liquidity problems as long as the stablecoins have enough collateral, especially when a large amount of the collateral is held as highly liquid assets.
Several stablecoin projects are already addressing the challenges of de-dollarization and enhancing financial inclusion. One example is the Stellar network, which uses its native stablecoin, Lumens (XLM), to facilitate cross-border transactions and provide low-cost remittance services. Another example is the MakerDAO project, which uses its stablecoin, Dai (DAI), to provide a stable store of value that is not subject to the volatility of other cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory Challenges
Stablecoins are still largely unregulated, and concerns about their potential impact on financial stability and consumer protection exist. Regulators around the world are grappling with how to regulate stablecoins. This is a concern since stablecoins are very different from conventional crypto. Stablecoins cannot survive as they do without special national regulations. Regulation is a highly jurisdictional issue since, as we can see, crypto laws do vary slightly in different countries.
In the U.S., stablecoin regulation could be more explicit, but the SEC needs to make that happen. The United States may be delaying their response because they intend to release the digital dollar. Additionally, several organizations, including the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OOC), and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), must apply their own federal rules to stablecoins. In addition to federal requirements, states may have their own rules, further complicating the situation.
Japan has been seeking to regulate cryptocurrencies uniformly. However, because of their peculiar character, stablecoins are expected to undergo special regulation, much as the nation may not even regulate the U.S. dollar-pegged Stablecoins as cryptocurrencies; instead, laws may be based on the real asset they are backed by.
In a developed nation like Singapore, stablecoins are said to comply with legal requirements if the Securities and Futures Act (SFA) is applicable. Before creating a stablecoin there, one must take caution because they come under such regulations. The digital asset shouldn't have any issues functioning in the Singaporean economy if it can comply with certain regulations.
Regarding stablecoin regulation and cryptocurrency in general, Russia has been highly erratic. The nation declares that particular "digital rights" laws put out by the government in 2019 must be followed by crypto-related crowdfunding platforms and projects. Stablecoins are not specifically mentioned in this law; thus, it is reasonable to presume that the same restrictions apply to assets backed by fiat as well.
General Guidelines Regarding Stablecoin Regulation
You are now aware of the many regulations that apply to stablecoins. But because cryptocurrencies are a worldwide commodity, it's critical to recognize the global legislation parallels. Fiat-backed currencies, for example, all plainly emphasize the transfer of value. Therefore, governments will need to ensure that parties may use stablecoins without risk. To prevent these transactions from being utilized for tax avoidance, they will also need to declare them.
The issue of what to do with the stablecoins follows. Some people could utilize them to send money overseas for payments. Others could view them as an alternate means of holding and investing in commodities like gold. Finally, these nations must consider global stablecoin law. In other words, they should observe how other countries accomplish the goals they seek to achieve. Authorities must also discuss if a single worldwide regulatory approach is preferable to several separate ones.
Stablecoins have emerged as an alternative to traditional currencies, offering stability, security, and transparency. In the context of de-dollarization, stablecoins have the potential to play a significant role in navigating the future of the global economy. However, several regulatory challenges and opportunities must be addressed to ensure widespread adoption. As the world shifts away from the U.S. dollar, stablecoins will become increasingly relevant, providing a secure and stable means of conducting cross-border transactions, investments, and hedging against currency fluctuations.
This article is provided for informational purposes only. It is not offered or intended to be used as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.

Tim Moseley

.png)




 .
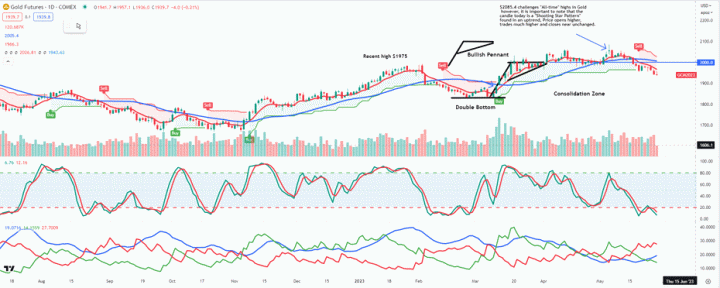
.
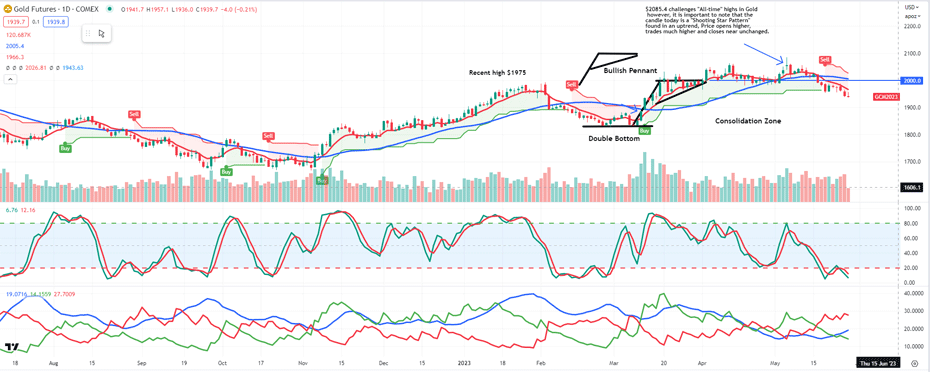
.gif)



.png)

(27).gif)

