
The Battle for Control: Why Governments Fear the Decentralized Nature of Bitcoin

Why is the government wary of Bitcoin? The simple answer to that question is "the loss of control!"
The government's most potent instrument for influencing the economy is controlling the money supply. The government wants total economic control because doing so would be politically advantageous. To make fresh money, the government borrows from banks. As a result, the government is increasing the amount of future debt that must be repaid to produce fiscal stimulus.
Thankfully, the government may depreciate the currency by reducing the debt's value. You get into trouble because you could want to hold onto the money as a store of value. Your savings will eventually lose value even if you have placed your funds in an interest-bearing account.
Governments are willing and ready to fight Bitcoin and other altcoins, not the blockchain technology that powers it. Several governments and banks have praised blockchain technology's workings, and they are keen to incorporate it into the system to move toward improving operational effectiveness.
Governments worldwide are preparing to implement digital currencies (CBDC) to simplify the electronic transfer procedure. The government intends to use blockchain technology so that digital transactions are traceable and can be taxed because it records every transaction in the ledger. The caveat is the type of blockchain they will implement for their digital currencies. It is permissioned, so only central banks will see the transactions, not the public.
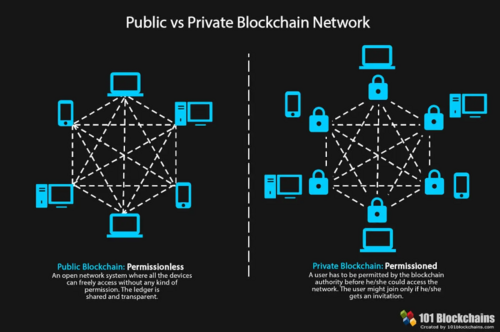
Image source: 101 Blockchains
People's confidence was shaken by the tremendous financial crisis that the world was experiencing. Once the banking system fell, Bitcoin rose from the ashes, giving consumers a different way to control their money. Anybody with an internet connection may buy Bitcoin and safely save their money. Peer-to-peer technology powers the payment network. It is a decentralized coin that the government, and any third parties, cannot manipulate.
Fiat currencies credibility
Fiat refers to the traditional currency issued by the government. The government has declared that these currencies are valuable. People have understood that this pledge is meaningless because real assets do not back fiat currencies over time. Fiat money typically lacks both intrinsic value and utility value. It only has value because those who use it as an accounting unit or, in the case of currency, a means of exchange believe it has value. They believe businesses and other individuals will accept it for transactional purposes.
You will never be able to trade the money in for a can of beans or a bar of gold with the government. People only believe in fiat currencies because the government has the credit to issue them. To purchase either of those items, you must pay the seller of beans or gold in fiat money.
Fiat currencies gained credibility through legal tender laws, central bank credibility, government backing, and the network effect. While a physical commodity does not support fiat currencies, it is backed by the government's ability to enforce legal tender laws and collect taxes, creating demand for the money. As long as people believe that the government will continue to back the currency and maintain its value, fiat currencies will continue to be accepted as a means of exchange.
The essence of control
Fiat money is totally under government control. They give central banks the authority to create or destroy money through monetary policy to affect the economy. The government also sets the rules for how these currencies may be moved so they can be traced and taxed. It makes it evident who stands to gain from this movement and aids in investigating illicit activity.
Control is necessary to ensure the safety and security of individuals and institutions. The government can set rules and regulations to prevent fraudulent or illegal activities, such as money laundering, and to protect consumers from financial scams or predatory lending practices. It also helps to prevent excessive speculation or manipulation of financial markets.
The government can regulate the money supply and influence economic activity by controlling the currency. By adjusting interest rates and using other monetary policy tools, central banks can help to stabilize inflation, support economic growth, and mitigate economic downturns. Central Banks like the Fed aim to protect the banks, giving them enormous powers to control the citizens. Money is power, and whoever controls the money controls power. This is exactly what the government wants.
How is Bitcoin valuable?
Long before Satoshi published his white paper on the Cryptography Mailing List in 2008, Bitcoin's history had already begun. Cryptographers first fought the battle for privacy and freedom in the digital era, then the Cypherpunks took up the cause, and now the Bitcoiners are carrying on the struggle.
Without question, Satoshi was brilliant, but he didn't create something from nothing. Instead, Satoshi shrewdly utilized existing technologies to produce the revolutionary new currency, Bitcoin. Note that because Satoshi Nakamoto chose to stay incognito, speculation has it that Satoshi could be a group rather than a single person.
Users of Bitcoin can escape the current financial system. Bitcoins don't actually exist in the physical world. They are produced by "miners" in cyberspace. Bitcoins are created by solving challenging algorithms that operate as a kind of global transaction verification rather than being written on paper or carved on metal.
This digital money (more accurately, cryptocurrency) can only be held digitally and transferred between buyers and sellers without an intermediary and is also awarded to miners when they correctly solve a block. The same idea applies to airline reward points on a more compact scale. The points may be used to pay for travel-related expenses like hotel and aircraft tickets. All of them utilize airline miles as virtual money.
The entire financial system's framework will collapse if Bitcoin is broadly embraced. This was a fantastic solution in light of the instances when the financial sector became corrupt.
In a research paper from Galaxy Digital, the energy used by the Bitcoin network was quantified and compared to that of other industries, such as the banking industry. It was discovered that while the banking sector uses 263.72 TWh annually, Bitcoin uses just 113.89 TWh.
By analyzing some of Bitcoin's distinctive qualities and how they relate to and affect its energy consumption, the research provided context for Bitcoin's energy usage. Regrettably, such important information won't be permitted to appear in the mainstream media due to the world powers' campaign against Bitcoin.
Why do governments fear Bitcoin?
- Unbeatable
When Bitcoin first emerged, many who opposed it painted it as a hoax. But Bitcoin is still there and in the news fourteen years later. There is always a long way to go before most people use Bitcoin. More businesses and services are embracing Bitcoin daily, making it a legitimate payment option. Anybody wishing for cryptocurrency to disappear will not get their dream since it is here to stay.
The loss of control presented by Bitcoin is a crucial issue that worries governments and financial institutions. They still need to devise a mechanism to tax Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency. The government cannot monitor the transactions or the revenue generated by them. You can see why the government discourages the idea, given that taxation is the primary source of governmental income.
The lack of a centralized authority and blockchain technology are the two defining characteristics of Bitcoin that give it power and acceptance. It establishes a secure network where users can remain pseudonymous. Yet when considered from the government's standpoint, this is a field it cannot regulate or meddle in. A lack of regulation for the government entails a lack of control and revenue.
Additionally, because Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer system, there is no need for a central clearing house or authority to oversee the transfers. What earnings are being produced, who is selling, and who is buying the Bitcoins remain entirely hidden from the sources, which is something the government hates so much.
- Provides a lifeline
Even the most essential products and services are sometimes unavailable to many in nations like Venezuela, which has suffered hyperinflation. Reports demonstrate how Venezuelans are surviving hyperinflation with the help of Bitcoin. They use this cryptocurrency to order internationally couriered items online. This nation illustrates how the people have been let down by the government and conventional banking institutions. Yet, the government has attempted to crack down on the Bitcoin miners and traders rather than finding a solution to the financial crisis.
- Community Control and Crime Concerns
The two-headed monster of government hostility to cryptocurrency is because it continues to remain out of their total control. Yet, it also suggests that they sincerely worry about protecting the rights of residents and those looking to invest in risky assets.
Having said that, it is crucial to remember that not all government worries are unwarranted. It was premised on the idea that financial transactions were anonymous, and thus criminal activity was inevitable. Crimes like drug trafficking, terrorism, money laundering, and tax evasion may worsen with such a system. These may harm the rest of society.
However, we must understand how Bitcoin can address the problems that traditional systems have caused, putting aside the likelihood of a wide variety of illegal acts that have garnered the headlines and painted them negatively. Recessions and unemployment have repeatedly been triggered by the central bank changing the money supply. The welfare of individuals is at risk because the global financial system thrives on avarice and corruption.
It's okay to try your luck with Bitcoin; remember that you're entrusting a very sophisticated system with your money. You may need to be more thoroughly knowledgeable about this industry; because you are interacting with individuals you don't know and entering a situation where you have few legal options.

The fight against Bitcoin requires large-scale coordination among nations
Bitcoin's growth has been a concern for various governments, including the United States. The US government is projected to run a $1.4 trillion deficit in 2023. Even if the government shuts down the entire military and eliminates the Department of Defense's projected $800 billion budget, the budget would still be projected to operate in the red for 2023.
This indicates that the U.S. government's resources to fight against Bitcoin are limited. Still, it is clear that the government is targeting cryptocurrency to expand the reach of its financial surveillance. Approximately 86% of central banks are actively exploring the development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). This development could threaten the growth of cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin.
Wall Street's push to open up access to Bitcoin investment is meeting resistance from a bipartisan group of lawmakers and regulators in Washington, which might also hinder the growth of Bitcoin. Some years ago, China, another country that has shown concern about the growth of Bitcoin, attempted to crack down on Bitcoin miners who effectively power the digital coins' accounting system by forcing its own banks to stop facilitating crypto use. If China can’t stop it, what do you think the countries that still practice freedom are going to do?
While the U.S. government's resources might be limited to fight against Bitcoin, the government might expand its arsenal through multilateral relations in targeting cryptocurrency to broaden the reach of its financial surveillance.
As Bitcoin is internationalized, effective regulation would require the cooperation and approval of practically every nation-state. Still, it might be challenging to see countries focusing on Bitcoin in unison; even though the major world powers such as the United States and China have a bloc-like effect, there has been more coordination, often led by the U.S. government.
Extensive cooperation is needed to shut down the network effectively; otherwise, users will successfully conduct transactions and maintain the Bitcoin network in other countries. A gradual, nation-by-nation prohibition might harm total acceptance.
At its most extreme, a very improbable state-led ban in the United States could prevent Bitcoin from accessing American-led financial institutions and markets with almost all global reach. However, a "global ban" or "government crackdown" will not be possible as Bitcoin can be used for transactional purposes across international borders.
The libertarian view
The allure of Bitcoin extends beyond its autonomy and financial stability. Digital money appeals to libertarians as well since they favor private property rights and minimal government involvement. Libertarians see Bitcoin as a method to avoid conventional financial institutions, which they believe are governed by governments and susceptible to heavy regulation. Bitcoin provides a decentralized financial system free from governmental control and inflationary monetary policies.
Because Bitcoin transactions are safe and transparent, they are consistent with libertarian values such as individual freedom and privacy. Bitcoin transactions cannot be controlled or changed thanks to permissionless blockchain technology, offering an unmatched level of security compared to conventional banking systems.
Bitcoin stands for control over one's financial future and the shielding of assets from governmental meddling for libertarians and those who share their views. Even if the appeal to libertarians may appear specialized, it is a sign that digital currencies can alter the financial landscape. It's conceivable that cryptocurrencies will become more widely accepted and used for various purposes as more people become aware of their benefits.
The bottom line
Governments are wary of Bitcoin for several reasons, including its lack of central control, illicit activity use, consumer protection, volatility, and potential threat to national currencies. While some governments have taken steps to regulate Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, others have banned them altogether. As Bitcoin continues to gain mainstream acceptance, it will be interesting to see different approaches to how governments respond to this new form of currency.
It's important to note that while governments are wary of Bitcoin, they also recognize the potential benefits of blockchain technology, which underlies Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Blockchain technology can potentially revolutionize various industries, including finance, healthcare, and logistics. The relationship between governments and cryptocurrencies is complex and evolving, and it will be interesting to see how it develops in the coming years.

Tim Moseley

