
World Economic Forum 2024 Global Economic Outlook: What Are The Chief Economists Predicting For Our Future?

2024 has been a year of elections as many countries worldwide have been gearing up for the polls. Nevertheless, as the campaigns and debates gain momentum, it's essential to remember that the popular vote has never chosen the individuals who wield the most significant impact on our daily lives. The World Economic Forum (WEF) is a prime example of this phenomenon. The WEF's ‘experts’ have been diligently crafting their newest economic prediction, which will inevitably have far-reaching implications that will affect everyone, regardless of our individual opinions.
This article analyzes the latest report from the WEF's chief economists, who express cautious optimism regarding the global economy's future. Despite their hopeful outlook, they anticipate various challenges ahead. However, a critical flaw in their analysis is the failure to recognize that the policies they promote often have adverse consequences for the general population. Ultimately, the WEF and its partners have overlooked a crucial aspect of the larger issue: their own role as a contributing factor to the problem.
The Economists’ View, Full Of Surprises Or Not
This article summarizes the "Chief Economists Outlook: May 2024" paper authored by numerous leading economists worldwide. This publication, updated quarterly, presents the collective views of these experts. The document commences with a brief overview, indicating that most economists anticipate a more robust global economy than the previous edition.
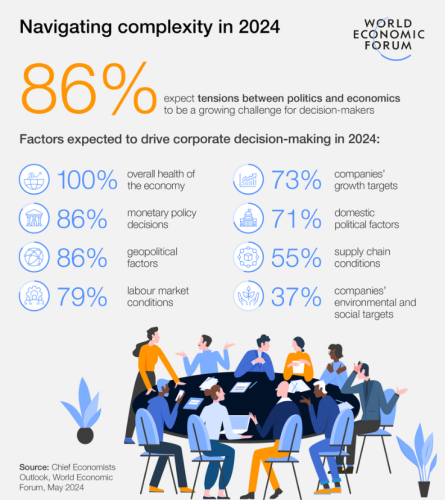
For perspective, in January, about 56% of economists thought the global economy would be weak. However, the latest data shows that only 17% share this belief. Not surprisingly, almost 100% of economists believe that geopolitics and politics will cause volatility. The elites appear to be particularly apprehensive about the possibility of a second Trump presidency.
It’s also not surprising that economists' prevailing view is that the US economy will maintain its strength while the EU's economy will weaken further. Surprisingly, they forecast that certain central banks, such as the European Central Bank, will cut interest rates, whereas others, like the Federal Reserve, will hold rates steady.
It’s also surprising that economists predict a global economic recovery in the next few years. It’s surprising because there’s a strong correlation between GDP and energy production, and many countries are not pursuing the best energy policies. The WEF is partially responsible for this situation.
According to the WEF's economic experts, these subpar energy policies are expected to boost economic growth miraculously. Ironically, their research reveals the actual sentiment on the ground, where numerous countries are skeptical about these policies' ability to stimulate economic growth. It's no surprise: they're unlikely to deliver.
Politics And Geopolitics
The paper's initial section reveals a prevailing consensus among WEF economists as “a mood of cautious optimism.” While many experts anticipate a thriving economy, the outlook is predicated on the assumption that political and geopolitical factors will not pose a significant threat to economic growth. The Middle East and Eastern Europe are currently the most pressing concerns regarding global hotspots. As we've witnessed, any intensification of the conflict between Israel and Hamas, along with its proxies, could have an even greater impact on oil prices.
The widespread use of oil in various industries would trigger a broad-based price surge, prompting central banks to maintain or increase interest rates to manage supply-side inflation effectively. The practical effect would make existing debts more costly and borrowing more challenging, ultimately leading to a slowdown in economic activity. It's worth noting that the economy already relies heavily on debt.
In Eastern Europe, the increasing tension is not primarily driven by economic factors as it is unlikely to cause additional disturbances to supply chains and similar aspects. Instead, the primary concern is that the situation could destabilize the region by casting doubt on the legitimacy of its institutions, both in the eyes of Europeans and other international actors. This is particularly relevant in light of the EU's consideration of releasing $300 billion in assets it seized from Russia to Ukraine.
It's worth noting that this move could have significant implications for the global financial system, potentially leading other countries to reassess their investments in Europe and European assets. To mitigate this risk, the EU has only released the profits generated by the seized assets rather than the assets themselves. However, the US is reportedly urging the EU to utilize the underlying assets to support Ukraine, and the EU is understandably cautious, given the potential for negative consequences.
In a related development, the US has been urging the EU to impose stricter measures on China. Taiwan is another potential hotspot that could trigger market instability. Notably, Taiwan is responsible for manufacturing most of the world's microchips, and any disruptions to its production or trade could have catastrophic consequences. It's intriguing that China has been escalating its hostilities towards Taiwan, suggesting it may not depend on Taiwan's unique microchip production capabilities.
Geopolitical experts speculate that China may have gained the capability to produce advanced chips independently, raising concerns about potential implications for Taiwan. Such action doesn't necessarily have to take the form of a full-scale invasion; a trade blockade would be sufficient to cause economic disruption. The fact that the US and EU are hastening to establish their own chip-making facilities suggests that such disruptions could be unavoidable.
On the political stage, a surge in nationalist parties has been unfolding globally, a trend that has been anticipated for some time. During difficult times, individuals often point fingers at the wealthy and immigrants. This sentiment seems true across various nations and challenges the globalist-focused economy because nationalist parties prioritize the interests of their citizens, for better or for worse. As highlighted in this article, globalism is failing, which will be painful in the short term. It will initially cause inflation to increase while asset prices remain high; wages will eventually follow.
The economists surveyed by the WEF anticipate that inflation will persist, and they attribute this to housing and energy rather than nationalism. Specifically, housing prices have increased due to globalist policies restricting construction and accelerating immigration, while globalist policies concerning energy have led to increased expenses across the board. According to the WEF's experts, prices may surge by 30% if tensions in the Middle East intensify.
They also note that a significant portion of global trade, 20-40%, occurs between geopolitically unaligned countries, which poses a challenge for European and Asian economies. Hopefully, the WEF’s economists' forecast regarding the Middle East isn't an accurate prophecy.
Unpredictability, Complexity, ESG
In the document's second section, economists from the WEF expand on the “challenging Global landscape.” They highlight how international conflicts, domestic strains, technology, and high interest rates have led to an unpredictable environment for everyone. For those unaware, investors generally dislike uncertainty more than any other factor. Investors don't mind a world war so long as it's certain because they can price it in and plan.
So far, the impact of this unpredictability has been relatively subdued, likely due to investors' assumption that the money printer will be turned back on. However, from the WEF and its economists' standpoint, the problem is not unpredictability; it’s complexity. The above factors contribute to this complexity, posing challenges for the WEF central planners' decision-making. In reality, they shouldn't be making these decisions in the first place.
WEF economists are concerned about the growing divergence between the data reported by governments and the actual experiences of individuals. In their own words, they quote, “The emergence of divergence between modestly encouraging economic data and stubbornly gloomy public sentiment.” This disparity has been described as a "challenge" by the WEF's economists, who have refrained from advocating censorship to address the issue in the name of misinformation, disinformation, etc. If this challenge continues, though, don't be surprised to see such censorship.
Adding fuel to the fire, the WEF's economic experts appear oblivious to the underlying reasons behind this growing disparity. They attribute it to simply being a matter of inequality and uncertainty, which barely begins to address the issue. It's becoming increasingly clear to many that the system is unfairly skewed in favor of the WEF itself. A prime example of this bias is a section in the report outlining the factors that will supposedly influence business decisions, as the WEF's economists dictated. This section of the paper outlines the factors affecting business decisions as perceived by the WEF's economists, which provides a telling example.
To clarify, businesses were not directly questioned; instead, a panel of academic experts was consulted to provide insights into businesses' perspectives. The responses were unsurprisingly disconnected from reality. For instance, WEF economists believe that typical businesses consider geopolitics in their day-to-day decision-making. In fact, most companies focus more on inflation and labor issues rather than geopolitics.
Interestingly, the study's authors rank labor as one of the least significant factors for businesses, which contradicts many businesses' actual priorities. This disconnect may explain why ordinary individuals are pushing back on the policies of those in power.
It's intriguing that the WEF's economists discovered that corporations are increasingly issuing as many bonds as possible. They believe these companies are apprehensive about what lies ahead, which suggests that they are concerned about the future and are borrowing heavily to prepare for future challenges.
In a more optimistic light, the WEF's research revealed that a majority—75%—of top business leaders harbor doubts about ESG principles, while nearly a quarter have rejected them altogether. This finding is noteworthy, especially considering that ESG has gained widespread traction in recent years, largely thanks to the efforts of influential asset managers such as BlackRock.
The WEF's economists then pivoted to another pressing issue: fiscal and monetary policy. Fiscal policy encompasses government spending and taxation, while monetary policy involves central banks and interest rates. As previously mentioned, the WEF's economists predict that interest rates will decrease in the EU while remaining relatively stable in the US and other regions.
Previously, central banks worldwide had aligned their monetary policies to mirror the actions of the Fed. This was done to avoid potential repercussions such as Japan's significant yen depreciation when central banks implemented divergent interest rate strategies. The European Central Bank faces a similar risk with the euro, as it may not be sustainable for the ECB to maintain elevated interest rates for an extended period. Oddly enough, economists at the WEF anticipate a trend towards more constrained fiscal policies, as governments apart from the US seem restricted in their ability to increase spending.
The projection for Europe is particularly surprising, considering the EU's strong commitment to funding ESG-related initiatives. What's most peculiar is that the paper's authors are puzzled by the expectation that the EU will reduce its spending. The discrepancy between monetary and fiscal policies in the Eurozone is believed to be a contributing factor. If not managed carefully, this could lead to the euro's collapse. That's why the ECB hastened the rollout of a digital euro to oversee the European economy.

Source: World Economic Forum
WEF Predictions, Policies
In the third section of the report, the WEF economists offer their projections for the future of the global economy. These predictions focus on the long term, specifically the next five years, which makes sense as it aligns with the WEF's goals it’s trying to achieve by 2030. Notably, the WEF's economists observe that global growth has slowed since the turn of the century.
They are significantly concerned about the possibility of a further deterioration in this global slowdown. This anxiety stems from the fact that almost 25% of the economists at the WEF think that the world will not be able to reach its pre-pandemic annual growth rate of 4%. This pessimistic outlook could be driven by varying perspectives on how much technologies such as AI can enhance productivity, with half of them expressing doubt about its significant impact.
The realization is striking, as the WEF has been optimistic about technologies such as AI due to their implicit promise to replace the populace and preserve the world's marvels exclusively for the privileged few. They still believe AI will drive growth, but not to the extent they initially anticipated.
A notable observation is the disparate way the WEF's economists perceive the impact of advancements like AI on developed and developing nations. Their perspective suggests that developed countries will reap the most significant benefits. In contrast, developing countries will only experience limited and incremental improvements as if this disparity was intentionally designed into the system.
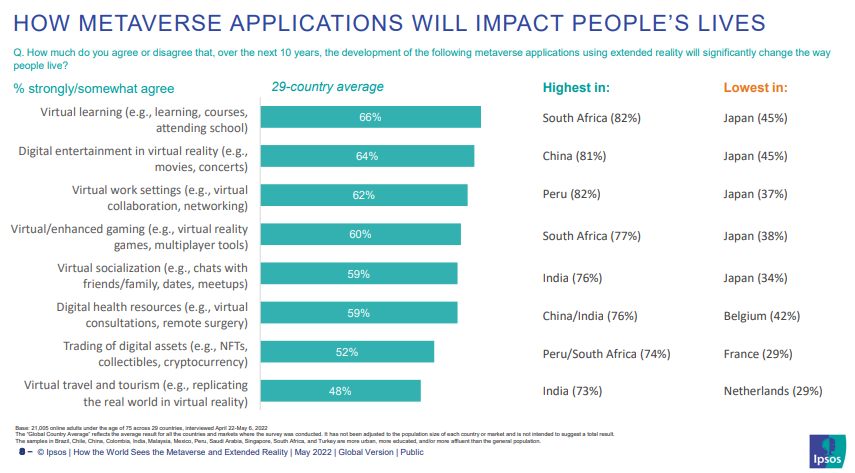
In 2022, an alarming headline emerged stating that, based on a survey conducted by the WEF, individuals in developing nations have a strong affinity for the metaverse. This assertion appears counterintuitive, suggesting a concerning implication that the WEF may be aiming to keep these countries in their place. This sentiment is also reflected in the WEF economists' paper.
Consider the following quote:
“There was a lack of consensus on the role of other industries, including mining, supply chain and transport services, manufacturing, fossil fuel energy and materials, retail and wholesale of consumer goods, and financial professional and real estate services in global growth.”
Consider that mining, manufacturing, and fossil fuel industries are the foundation for many developing nations. Notably, WEF economists hold differing views regarding these industries, even though they are essential for the advancement of developed countries. After all, artificial intelligence relies on hardware.
The paper's concluding section focuses on the crucial aspects of policy priorities that will foster economic growth in the next five years. The WEF economists emphasize the significance of these policies, which are likely to be adopted by most countries, given the significant influence the WEF wields over government decision-making processes.
It's a bitter irony that the WEF's economists claim that the global economy could have grown by an additional 50% if capital had been allocated more efficiently in recent years. What's striking is that they seem oblivious to the fact that their own policies have created an environment that encourages this misallocation of resources. This oversight raises severe concerns about the kind of misguided policies we can expect from the WEF and its political cronies. The nature of these policies will likely vary depending on whether they are aimed at developing or developed economies.
Developed countries will prioritize education, infrastructure, improved financial access, and institutional development. While this may seem positive in theory, in reality, education can lead to indoctrination, infrastructure can result in dystopian technologies such as digital IDs, access to finance can mean giving control of your money to a single entity like Black Rock, and more institutions can translate to more unaccountable and unelected organizations influencing domestic affairs.
The economic policies advocated by the WEF economists are similar for developing countries, with a minor variation: innovation. While innovation is a crucial factor in developed countries, it supposedly has less impact in developing countries. At first glance, this might seem like an anomaly, but it actually reveals a more profound truth.
The economists at the WEF emphasize that implementing trade protectionism would have adverse effects regardless of a country's economic situation. In other words, don't you dare put the well-being of your population above our profits. Observing the outcomes for countries that choose this approach will be intriguing.
Economists' Trustworthiness: A Call for Critical Thinking
It is necessary to acknowledge that economists may not always tell the truth when delivering information to different audiences. Therefore, it is wise to approach the content of this paper with caution, as economists are known to provide misleading information to the general public. Nevertheless, the statements made by the WEF economists hold some truth. The global landscape is facing growing instability due to geopolitical and political challenges. However, the underlying concern goes beyond this surface-level analysis, pointing to the inherent instability of centralization.
Visualize the process of stacking coins one on top of the other. Initially, the stack is steady, but with each additional coin, the stability decreases. Adding supports can temporarily enhance stability, but the more coins you stack, the greater the instability, leading to an inevitable collapse. This illustrates that instability is a fundamental characteristic of centralization. It's easy to overlook that centralized systems, such as those developed by organizations like the World Economic Forum, have been in development for decades.
As their rigid structures have grown increasingly fragile, those in power have tightened their grip, but the populace has reached their breaking point. The positive development is that a growing number of people recognize that the challenges they encounter are a direct result of the systems established by influential organizations like the WEF rather than being caused by scapegoats like immigrants, the wealthy, or politicians themselves. The downside is that the WEF is aware of this growing awareness and is unlikely to take it lying down.
Censorship has been on the rise, and although there are still some areas where individuals can express themselves freely and gather peacefully, these spaces are being threatened from multiple directions. Legal action, regulations, market manipulation, and infiltration by WEF-affiliated entities applying the usual totalitarian tactics contribute to this trend. The irony is that as these tactics become more brazen, they risk fueling a growing distrust of institutions, potentially leading to a breakdown in social order and widespread chaos.
Let's not be naive; the World Economic Forum would seize this opportunity, and some believe it's actively working to bring it about. The WEF has explicitly advocated for a global reset since the pandemic outbreak. Although its efforts have been unsuccessful so far, it's unlikely to give up. The only way to achieve a reset is to dismantle the current system, and we may be inadvertently playing into the hands of those planning a deliberate collapse.
Speculation aside, the answer to the current problem is establishing a new framework composed of decentralized organizations crafted for and by the average person. This is the vision that the cryptocurrency sector strives to realize, and it's why the World Economic Forum has been attempting to insert itself into the process. Thankfully, those committed to creating decentralized platforms and institutions are not the type that would ever collaborate with the WEF, no matter the reward. Countless individuals are dedicating their time and effort to this endeavor, and if you wish to effect genuine change, consider joining them.

Tim Moseley








(32).gif)




(29).gif)