
FATF Out To Get Crypto. FATF Travel Rule Expanded. What Does It Mean For Crypto?

The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has been making portentous noises about crypto in recent years, and several countries are getting antsy. The most prominent concern is implementing the “travel rule,” designed to force crypto companies to collect information about any transfer of digital assets worth more than US$1,000. Some countries, notably the UK, have in the past pushed back against this ‘recommendation’ from the FATF, but their resistance now appears to be wavering. The FATF is on the warpath and has crypto firmly in sight.
This article examines what the FATF is up to, what it could mean for your country, and what it all means for crypto. Although it may sound like more doom and gloom, there are reasons to believe that crypto could benefit from the FATF’s meddling in some ways.
Just recently, PayPal announced that it would prevent UK users from buying BTC until early 2024. PayPal reportedly did this because the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) so-called travel rule requires all crypto companies to collect detailed info about crypto transfers. The travel rule was set to go into effect in the UK on September 1st, 2023, and is being rolled out worldwide. This could have a profound impact on crypto companies and projects everywhere.

Image Source: Coindesk
What Is The FATF?
The Financial Action Task Force, or FATF, is an unelected and unaccountable international organization based in Paris, France. It was created by G7 countries in 1989 to combat money laundering, but its scope has expanded significantly since then. However, these recommendations have apparently done nothing to combat illicit financial activity over the last 30 years.
The organization adopted a mandate in 2019 to “Combat any threats to the integrity of the financial system.” Of course, the FATF considers crypto a threat, probably because its purpose is to replace the financial system. The FATF started applying its so-called recommendations to the crypto industry in 2019, and any country that refuses to go along with these recommendations will find itself cut out of the international financial system. The FATF finalized its recommendations for cryptocurrency in October 2021.
FATF’s Crypto Recommendations
The FATF’s crypto recommendations involve labeling everything that doesn't involve a third party as “high-risk.” This includes holding your crypto in your wallet and sending crypto peer-to-peer. The FATF also considers any crypto privacy to be inherently high risk. If these recommendations are implemented as regulations, crypto will become another arm of the existing financial system. It will offer no financial freedom and no financial privacy. The only exception is NFTs, which are exempt from these recommendations for unknown reasons.
On that note, you should know that the FATF crypto recommendations only apply to intermediaries working with crypto, which the FATF refers to as Virtual Assets Service Providers or VASPs. The FATF’s crypto recommendations do not apply to miners, validators, or crypto wallets, at least not yet. However, the scope of the FATF's requests seems to have expanded over time, so this could change. This expansion is especially true of the travel rule, which requires VASPs to collect KYC on everyone who buys or sells more than $1,000 of crypto.
The Travel Rule Expanded
Crypto exchanges started collecting KYC in 2021. Since then, however, the travel rule has expanded to require VASPs to collect KYC-level information about crypto transfers to and from VASPs worth more than $1000. Note that it's not entirely clear when the scope of the travel rule was expanded. Research suggests this expansion happened after the FATF’s finalized crypto recommendations were published in October 2021. Some may recall that South Korean crypto exchanges started forcing users to provide KYC-type information for crypto wallet transfers in December 2021.
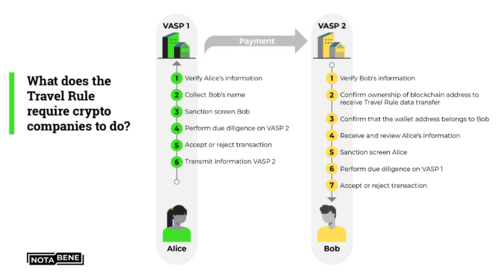
Images source: Notabene
The good news is that some countries have pushed back against the expanded travel rule. You might remember that the UK announced that it would not force VASPs to track transfers to and from crypto wallets in mid-2022, stating that they did not pose any illicit activity risks.
The not-so-good news is that these countries, notably the UK, seem to have pulled a 180â°. As mentioned, the UK implemented this expanded travel rule starting September 1st. The announcement specified that it did this in response to a statement by the FATF in June 2023. The FATF announcement called on countries to implement its crypto recommendations as regulations “without delay.” Of course, this is not a recommendation; it's a demand. Comply with our crypto recommendations, or we will restrict your access to the global financial system.
Some countries could not comply, so they had to ban crypto. Two countries that did this are Pakistan and Kuwait, both of which recently banned crypto in its entirety, citing the FATF’s crypto recommendations as the reason. It appears that the UK opted to comply instead.

Image source: Notabene-Regulations
Which Countries Are Now Affected
So this begs the question of when the FATF's expanded travel rule is coming to your country. The answer depends on the country; a complete list of countries and their compliance with the expanded travel rule can be found on the website of Notabene, a crypto compliance company. If you look at the list, you'll notice that some have already implemented the travel rule. It shows that not all have implemented the expanded travel rule. You'll have to click the link on your country and look at the details.
There's only one country we need to look at: the United States. That's because the US heavily influences the FATF. The travel rule has its roots in the United States’ Bank Secrecy Act. KYC, for financial transactions, originates in the infamous Patriot Act. The FATF’s finalized crypto recommendations were even co-authored by the US Treasury Department. As such, it's safe to assume that the FATF’s crypto recommendations are likely to mirror similar regulations that are being proposed or that have already been passed in the United States.
The FATF's expanded travel rule seems rooted in an infamous FinCEN proposal from November 2020. The proposal was to lower the travel rule transaction threshold from $3,000 to just $250 and expand its scope to include any crypto transactions. This includes transfers between crypto wallets and VASPs, i.e., exchanges. There is also an outcry on the measure of invasion of privacy,
Fortunately, this proposal has yet to be approved. Unfortunately, the US has influenced the FATF to implement this proposal in other countries instead. That's because the travel rule transaction threshold in jurisdictions like the European Union is $0, which the FATF suggested in its finalized crypto recommendations. This is more significant than you might think because it indicates the start of a very slippery slope.
A Slippery Slope
First, the FATF just wanted VASPs to complete KYC on their users. Now, they want VASPs to get info on crypto transactions above a specific value. Eventually, they'll require VASPs to get information on all crypto transactions, and the countries that don't force VASPs to comply will be cut out of the global financial system. This ties into why some countries, such as Kuwait and Pakistan, ban crypto instead of complying with the FATF, like other countries, such as South Korea and the UK.
The answer is likely because they lack the resources to comply with these recommendations. Take a second to consider that information about all these travel rule transactions will have to be shared with national regulators. In turn, these national regulators will have to make sense of this massive amount of information and understand which transactions could be illicit and which ones are legit. If they fail to do this to the standard that the FATF wants, they could just as easily find themselves on the FATF’s grey list or even black List.
In other words, the outcome of attempting to comply will be almost the same as outright non-compliance. So why bother trying to comply? Not only that, but it's possible that the US would use this alleged non-compliance as justification to punish its geopolitical opponents. For context, it's believed that up to 40% of money laundering occurs in the United States, yet countries like the UAE are ending up on the FATF's naughty lists.
Is it Geopolitical, for Profit, or Something Else?
Given this fact, one could argue that the primary purpose of the FATF is geopolitical, not regulatory. If this is the case, it's appalling because it means the US is using the FATF to push its allies to comply. Remember that the UK initially wasn't going to apply the FATF's expanded travel rule. This relates to why any country would take the risk of complying with the FATF crypto recommendations instead of just banning crypto.
Some say the answer is probably profit. Crypto has unprecedented potential; dozens of countries are trying to capitalize on this by becoming crypto hubs. The paradox is that the FATF's expanded travel rule alone is likely enough to crush smaller crypto companies and startups. That's because they would need more financial resources to comply. This would mean that the large crypto companies left standing could become monopolies.
At that point, it would be effortless for the FATF to expand the purview of its crypto recommendations again to outlaw self-custody, peer-to-peer transactions, and crypto privacy completely. Again, this would turn crypto into another arm of the existing financial system, making it much more dystopian.
How Could It Benefit the Crypto Market?
The silver lining is that this outcome is years away from occurring and is not guaranteed. It could also benefit the crypto market in short to medium term. That's simply because institutional investors will likely invest more in crypto once all these FATF-based regulations are in place. This is because crypto would become ever so slightly more integrated with the existing financial system from a regulatory perspective.
This means more crypto to fiat on and off ramps, more funding for crypto projects and companies, and more direct crypto investment. The consequence is that crypto would no longer become a niche asset class, making self-custody and peer-to-peer transactions more common.
Under normal circumstances, this would result in an explosion of crypto-specific innovation, like new DeFi protocols, for instance. However, under the FATF's recommendations, any crypto projects or companies offering these innovations would be under extreme scrutiny. Unless they're perfectly decentralized, the FATF will label them all as VASPs and force them to comply with recommendations like the travel rule.
Believe it or not, this will also benefit crypto because it will force new crypto projects and protocols to be as decentralized as possible to outmaneuver the FATF. This will be painful in the short term because crypto projects and companies are not very decentralized. An explanation of what it means to be genuinely decentralized can be found here.
That said, if any genuinely decentralized crypto projects and protocols managed to gain significant adoption, the FATF would likely respond by further expanding the scope of its crypto recommendations. In a recent report, Notabene noted that the FATF left the door open to this possibility, citing,
“Transfers between self-hosted wallets, so-called peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions are not explicitly covered by AML/CFT rules. The FATF opens the door to a future paradigm change in case there is a distinct trend towards P2P transactions.”
Translation: If actual cryptocurrency, that is, peer-to-peer trustless transactions, becomes too popular, then the FATF would respond by saying wallets that engage in crypto activities are high risk. In practical terms, this could mean not being able to transfer crypto between such wallets and a compliant VASP. What's funny is that this would likely result in a parallel financial system, which is precisely the opposite of what the FATF is trying to achieve with its crypto recommendations.
On that note, fully decentralized crypto-based communities in social media, marketing, and digital broadcasting are rising and in the throes of building a parallel economy. Given the privacy and censorship issues of legacy social media, governments, woke agencies, and tech corporations, with their propensity to ban or suspend their services to individuals and companies that go against their narrative, have brought this imperative to the fore.
Is the Crypto Industry Complying?
So, what is the crypto industry doing about the FATF crypto recommendations? Well, at first glance, it looks like it’s complying; upon closer inspection, however, this compliance has been incredibly strategic. To explain, the crypto industry took its time complying with the FATF crypto recommendations. After all, compliance is an additional cost, and most countries were not pressuring them about compliance with the FATF until recently.
There are technically no deadlines for compliance with the FATF’s recommendations. In theory, countries must apply the FATF recommendations within one year of their announcement. In practice, most countries don't. One expert explained that the travel rule was a bit of a myth. Just 10% had implemented the crypto travel rule in 2022, but in all fairness, this apparent non-compliance wasn't intentional.
The FATF has constantly been adjusting its crypto recommendations to account for changes in the crypto industry. Everyone started taking them seriously only after the finalized crypto recommendations were published. This includes the crypto industry, which, according to Notabene’s survey, “seemed willing to adopt the travel rule in January 2022.” By then, some of the biggest entities had already started exploring travel rule compliance, like USDT issuer Tether and its sister exchange Bitfinex working with Notabene.
Here's where things get interesting: Notabene, the crypto compliance company, has been referenced by the FATF on a few occasions. This is surprising, considering that the company has received most of its funding from the crypto industry, according to Crunchbase.
Also, according to Notabene, the criteria used to determine which crypto transactions are considered high-risk from the FATF's perspective is determined by blockchain analytics companies, not Notabene itself. The largest is Chainalysis, which is very pro-crypto. In fact, Chainalysis pushed back against the FATF’s crypto recommendations when they were first proposed in 2019.
The institutions the FATF relies on to implement its crypto recommendations are all pro-crypto. To put things into perspective, companies like Notabene and Chainalysis have been advising governments and regulators. Put another way, the impact of the FATF crypto recommendations may not be as anti-crypto as they intend them to be because all the institutions required to implement them are pro-crypto. It's not just private companies; some countries are also trying to protect crypto.
Crypto Privacy in Jeopardy?
There's only one place where the FATF could still cause a problem: privacy. As most of us know, financial privacy is required for financial freedom. You can be coerced in many ways if every transaction is tracked. e.g., by punishing the people you transact with. Logically, it will be challenging for pro-crypto compliance companies and countries to defend crypto privacy from the FATF. This will be practically impossible when the FATF decrees that any exchange offering privacy coins is inherently non-compliant. It could result in the elimination of crypto privacy altogether.
Some would say the recent sanctions against Tornado Cash are a prelude to the FATF's next moves. Luckily, the crypto industry has been working on a solution, too. Notably, the FATF claimed that there had been a considerable move towards privacy in crypto in its finalized recommendations, stating, “During recent FATF consultations, the industry highlighted data protection and privacy (DPP) issues as key considerations for travel rule implementation…. Going forward, FATF will continue to monitor these issues to ensure data privacy and other similar issues do not present barriers to implementation.”
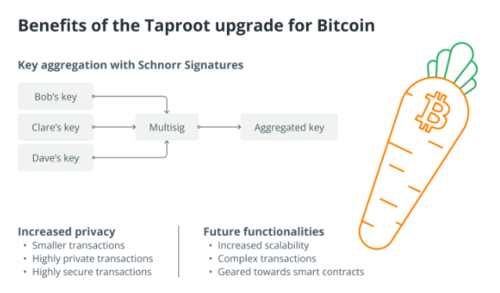
Image source: Cointelegraph
Crypto Privacy Predestined – The Solution
Besides the many crypto projects like Ethereum trying to preserve privacy through cutting-edge technology, like zero-knowledge proofs, Bitcoin has also been subtly working on privacy-preserving technology. The Taproot upgrade is one protocol developed in November 2021.
One of the things Taproot did was introduce Key Aggregation with Schnoor Signatures. Put simply, it made every single Bitcoin transaction look like a regular transaction. This move means that transactions involving multisig wallets resemble regular transactions on the blockchain. It’s significant because multisig wallets are required for Atomic Swaps, i.e., swapping BTC for a crypto coin on another blockchain. Incidentally, Monero developers finally found a way to execute swaps between BTC and XMR in August 2021.
Taproot means these swaps are now theoretically undetectable. Multisig wallets are also required for the lightning Network, Bitcoin's most significant Layer 2 protocol. As it so happens, US authorities offered bounties to anyone who could track XMR and Lightning Network transactions in September 2020. This implies that the Lightning Network has similar privacy levels to Monero.
Interestingly, the three Bitcoin Improvement proposals that make up the Taproot upgrade, including Schnoor Signatures, were all proposed in January 2020, shortly before the first countries started implementing the crypto travel rule. Is this a coincidence, or perhaps something more?
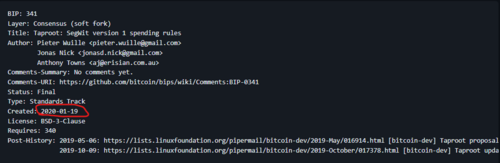
Image source: GitHub
Anyway, speculation aside, it's clear that crypto privacy is inevitable because nobody wants privacy more than high-net-worth individuals. When these investors get involved during the next crypto bull market, there will definitely be calls to increase crypto privacy, and many will be answered. Additionally, if these calls don't come from the 1%, you can bet they'll come from the central banks that will start accumulating crypto in 2025.
The regulated crypto space will likely grow, but the unhosted ecosystem will remain a niche area with significant development and innovation. The crypto and blockchain projects that uphold the interests of entrepreneurs and advocate for free and critical thinking are paving the way and developing ecosystems that will have the financial freedom, liberty, and sovereignty that is fundamentally our right of passage, which seems to be all but forgotten by the monopolies and so-called authorities and their mandate to capture the crypto industry.

Tim Moseley

(33).gif)




.png)






(31).gif)


.png)




.png)


.png)
(30).gif)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)




.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)




(28).gif)